Our anti-VGLUT1/2 reveal neuroprotective potential in brain ischemia
Pomierny B, Krzyżanowska W, Skórkowska A, Jurczyk J, Bystrowska B, Budziszewska B, Pera J. Inhibition of Vesicular Glutamate Transporters (VGLUTs) with Chicago Sky Blue 6B Before Focal Cerebral Ischemia Offers Neuroprotection. Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Jun;60(6):3130-3146. PMID: 36802054
Focal cerebral ischemia is a localized reduction or cessation of blood flow to a specific region of the brain, leading to oxygen and nutrient deprivation that can cause neuronal damage or death.
This study examines the neuroprotective potential of inhibiting vesicular glutamate transporters (VGLUT1 and VGLUT2) using Chicago Sky Blue 6B (CSB6B) in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia and evaluates the effects of CSB6B on glutamate release, infarct volume, and neurological deficits.
VGLUTs, crucial for glutamate loading into synaptic vesicles, contribute to excitotoxicity during ischemia. VGLUT expression was evaluated using RT-qPCR, Western blot, and immunofluorescence histochemistry, employing Anti-VGLUT1 AMAb91041 and Anti-VGLUT2 AMAb91081 PrecisA Monoclonals manufactured by Atlas Antibodies.
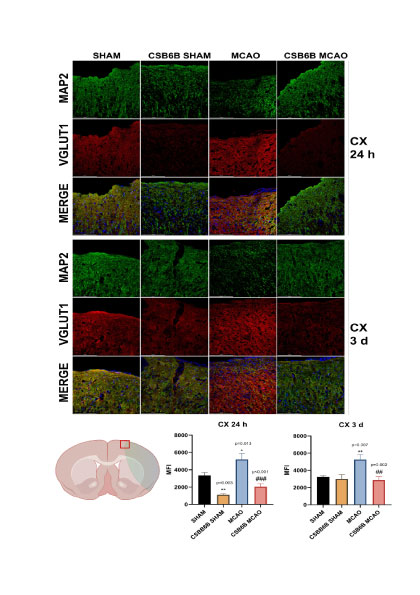
Results show that ischemia upregulates VGLUT1 and VGLUT2 in the cerebral cortex and dorsal striatum, while CSB6B pretreatment reduces glutamate release, infarct volume, and neurological deficits, matching the efficacy of ischemic preconditioning. CSB6B also decreasesVGLUT mRNA and protein expression in affected regions.
These findings highlight VGLUT inhibition as a promising neuroprotective strategy, though limitations like CSB6B’s non-specificity and inability to cross the blood-brain barrier suggest a need for more targeted therapies.
